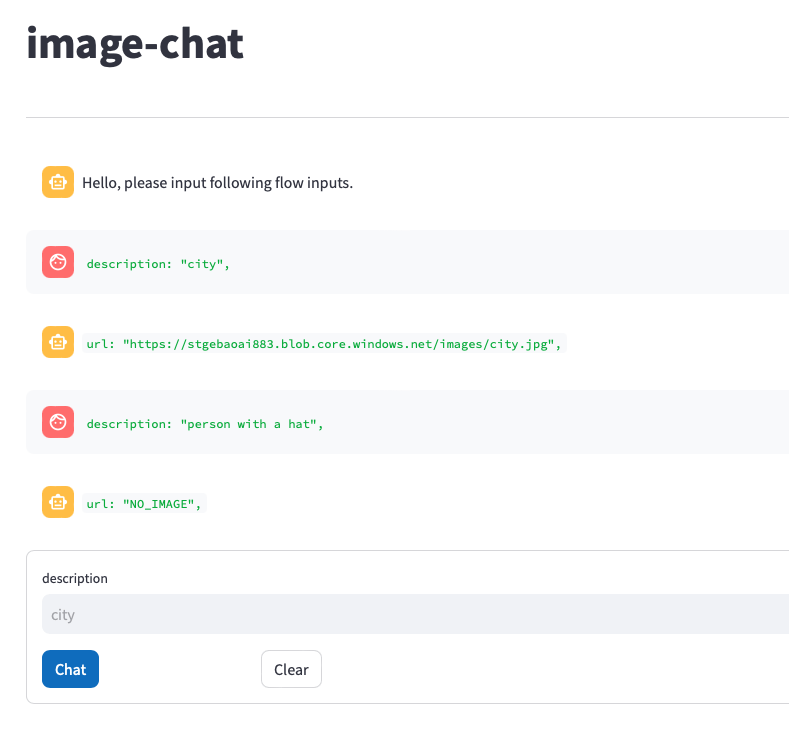
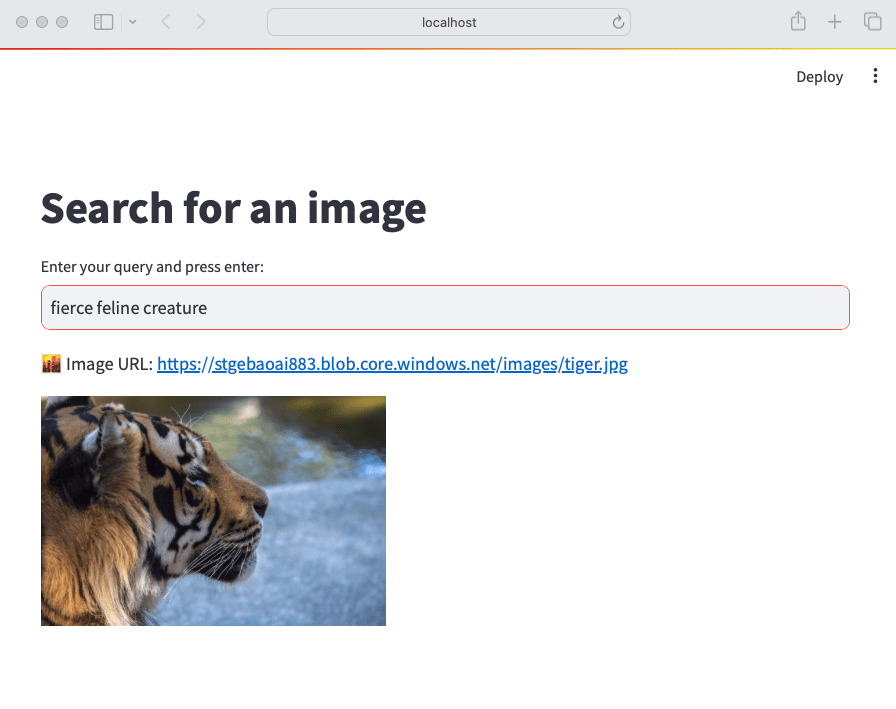
A while ago, I wrote about creating your first Prompt Flow in Visual Studio Code. In this post, we will embed such a flow in a Python application built with Streamlit. The application allows you to search for images based on a description. Check the screenshot below:
There are a few things we need to make this work:
- An index in Azure AI Search that contains descriptions of images, a vector of these descriptions and a link to the image
- A flow in Prompt Flow that takes a description as input and returns the image link or the entire image as output
- A Python application (the Streamlit app above) that uses the flow to return an image based on the description
Let’s look at each component in turn.
Azure AI Search Index
Azure AI Search is a search index that supports keyword search, vector search and semantic reranking. You can combine keyword and vector search in what is called a hybrid search. The hybrid search results can optionally be reranked further using a state-of-the-art semantic reranker.
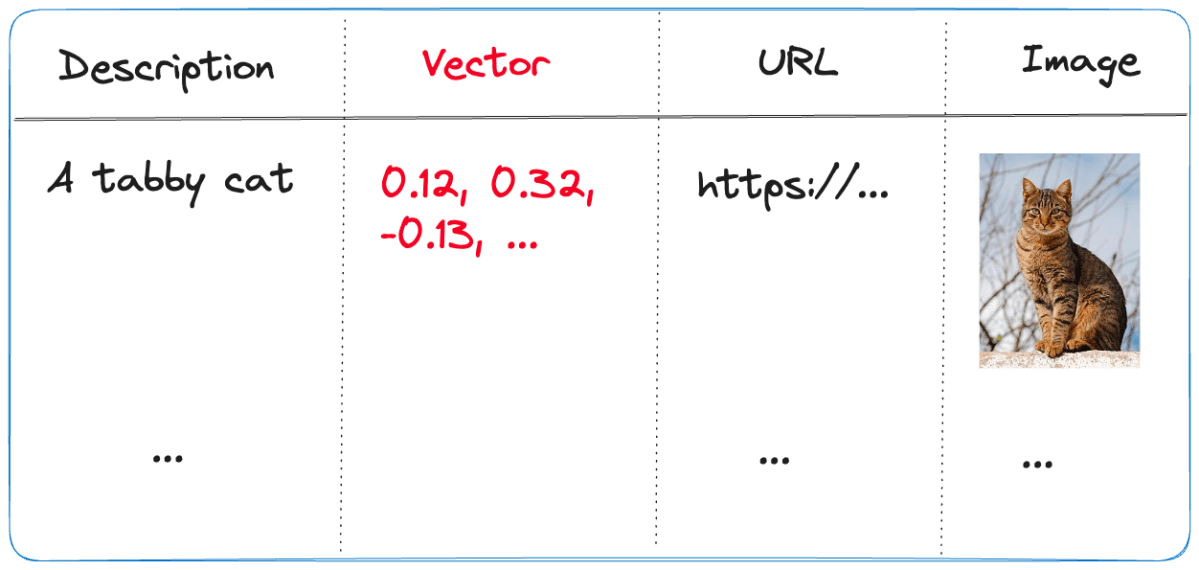
The index we use is represented below:
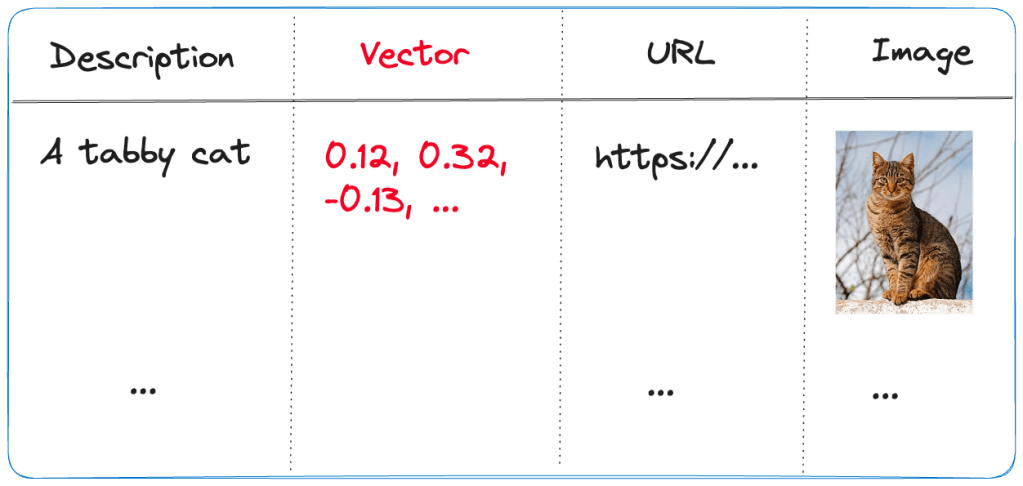
- Description: contains the description of the image; the image description was generated with the
gpt-4-visionmodel and is larger than just a few words - URL: the link to the actual image; the image is not stored in the index, it’s just shown for reference
- Vector: vector generated by the Azure OpenAI embedding model; it generates 1536 floating point numbers that represent the meaning of the description
Using vectors and vector search allows us to search not just for cat but also for words like kat (in Dutch) or even feline creature.
The flow we will create in Prompt Flow uses the Azure AI Search index to find the URL based on the description. However, because Azure AI Search might return images that are not relevant, we also use a GPT model to make the final call about what image to return.
Flow
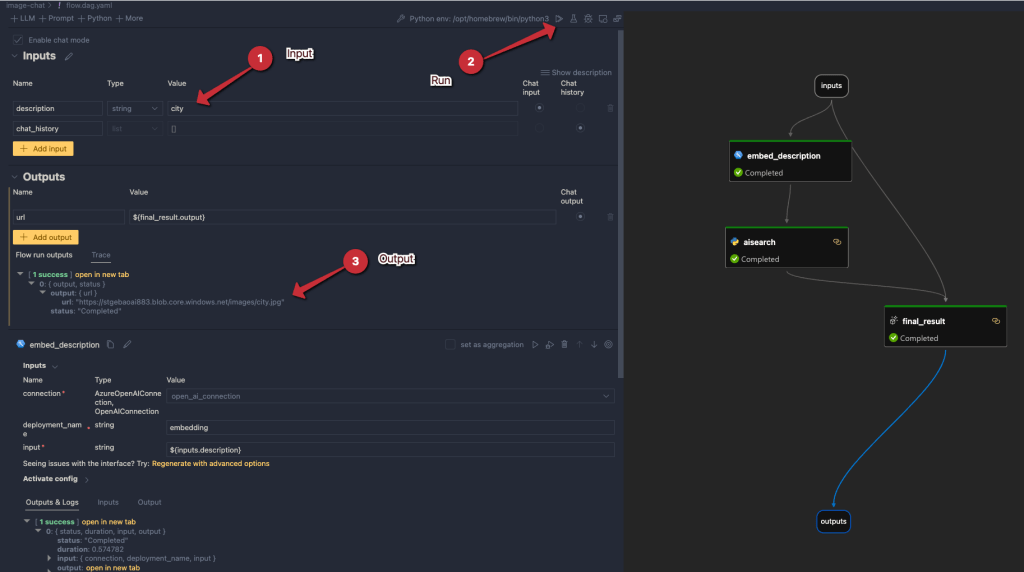
In Prompt Flow in Visual Studio Code, we will create the flow below:

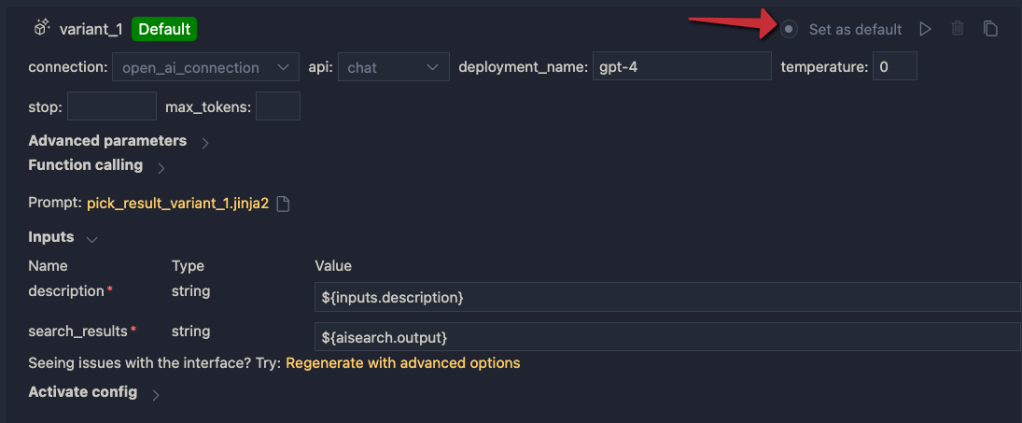
It all starts from the input node:

The flow takes one input: description. In order to search for this description, we need to convert it to a vector. Note that we could skip this and just do a text search. However, that will not get us the best results.
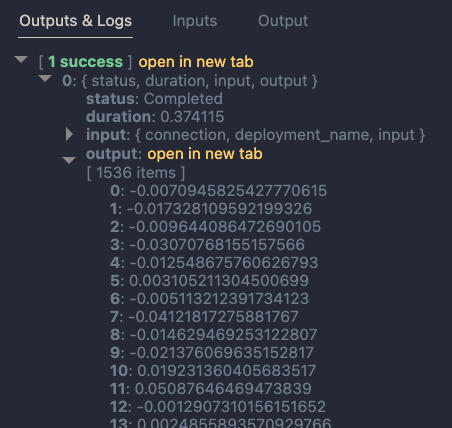
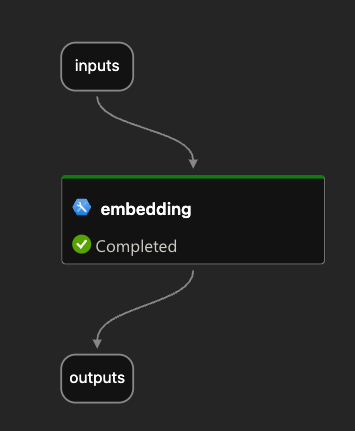
To embed the input, we use the embedding node:

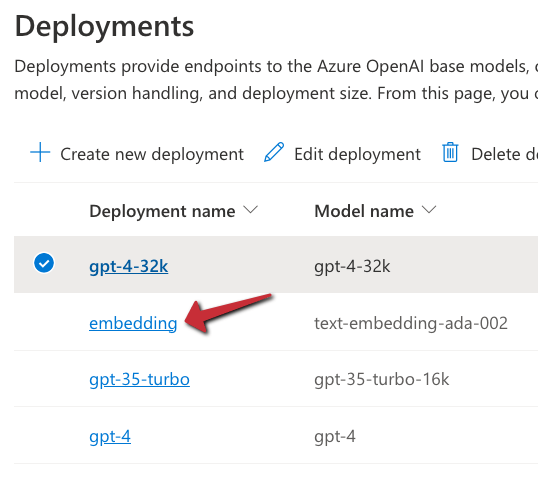
The embedding node uses a connection called open_ai_connection. This connection contains connection information to an Azure OpenAI resource that hosts the embedding model. The model deployment’s name is embedding. The input to the embedding node is the description from the input. The output is a vector:
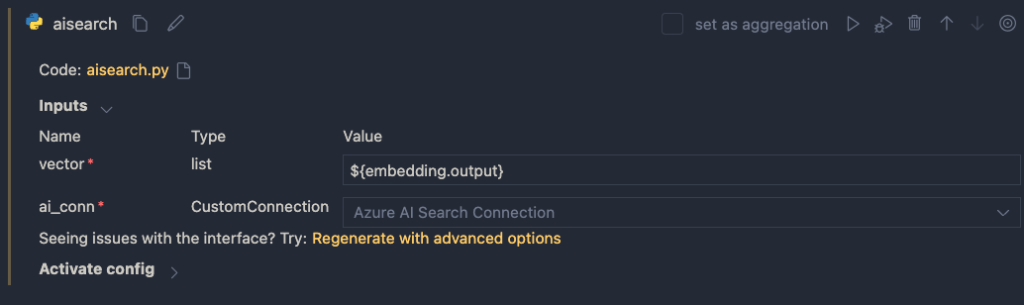
Now that we have the embedding, we can use a Vector DB Lookup node to perform a vector search in Azure AI Search:
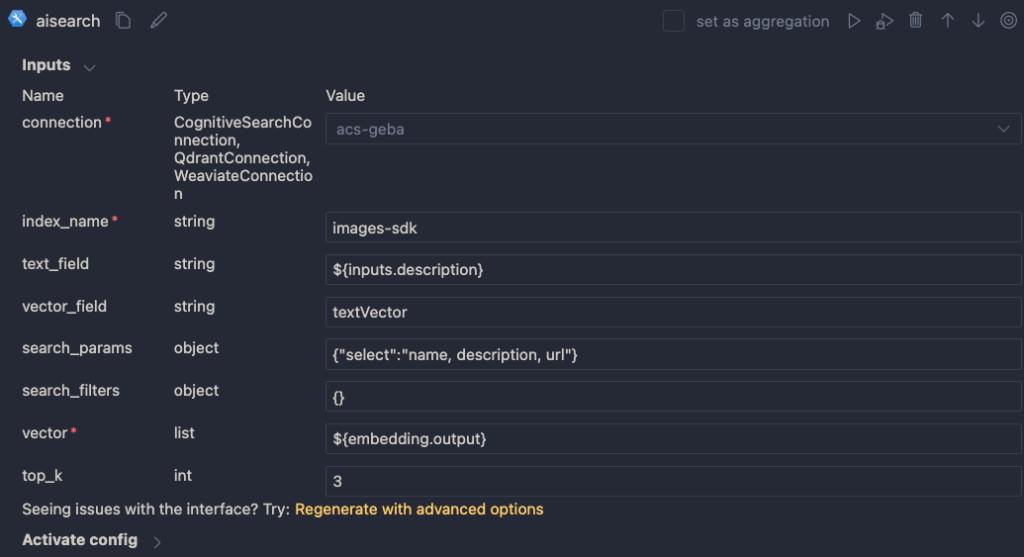
Above, we use another connection (acs-geba) that holds the credentials to connect to the Azure AI Search resource. We specify the following to perform the search:
- index name to search:
images-sdkhere - what text to put in the
text_field: the description from the input; this search will be a hybrid search; we search with both text and a vector - vector field: the name of the field that holds the vector (textVector field in the images-sdk index)
search_params: here we specify the fields we want to return in the search results; name, description and url- vector to find similar vectors for: the output from the embedding node
- the number of similar items to return:
top_kis 3
The result of the search node is shown below:

The result contains three entries from the search index. The first result is the closest to the description from our input node. In this case, we could just take the first result and be done with it. But what if we get results that do not match the description?
To make the final judgement about what picture to return, let’s add an LLM node:
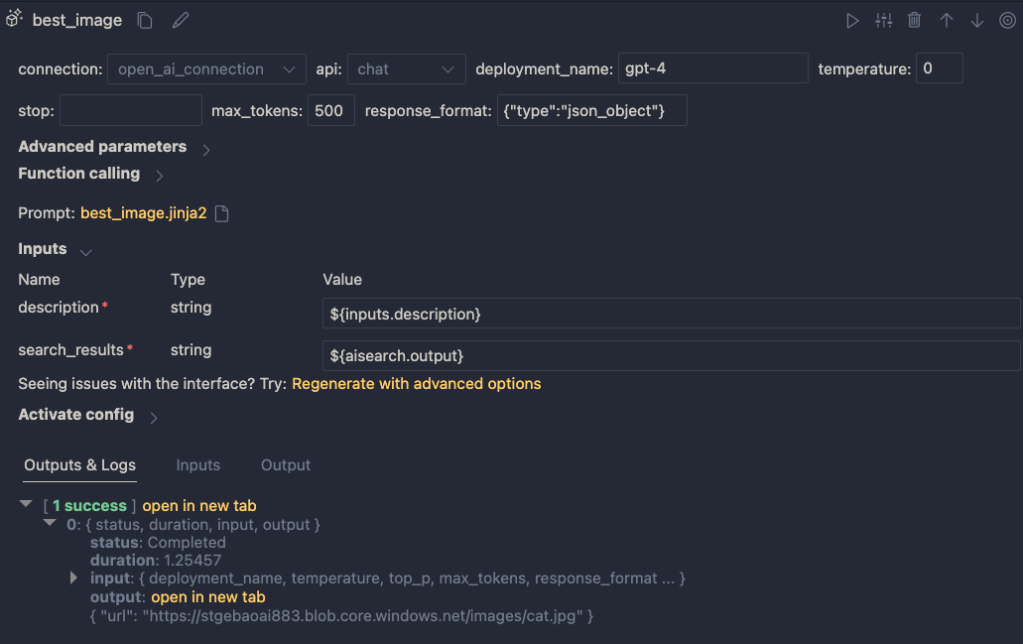
The LLM node uses the same OpenAI connection and is configured to use the chat completions API with the gpt-4 model. We want this node to return proper JSON by setting the response_format to json_object. We also need a prompt, which is a ninja2 template best_image.jinja2:
system:
You return the url to an image that best matches the user's question. Use the provided context to select the image. Return the URL in JSON like so:
{ "url": "the_url_from_search" }
Only return an image when the user question matches the context. If not found, return JSON with the url empty like { "url": "" }
user question:
{{description}}
context : {{search_results}}
The template above sets the system prompt and specifically asks to return JSON. With the response format set to JSON, the word JSON (in uppercase) needs to be in the prompt or you will get an error.
The prompt defines two parameters:
description: we connect the description from the input to this parametersearch_results: we connect the results from the aisearch node to this parameter
In the screenshot above, you can see this mapping being made. It’s all done in the UI, no code required.
When this node returns an output, it will be in the JSON format we specified. However, that does still not mean that the URL will be correct. The model might still return an incorrect url, although we try to mitigate that in the prompt.
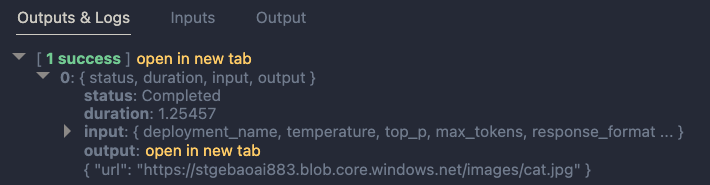
Below is an example of the LLM output when the description is cat:
Now that we have the URL, I want the flow to output two values:
- the URL: the URL as a string, not wrapped in JSON
- the base-64 representation of the image that can we used directly in an HTML IMG tag
We use two Python tools for this and bring the results to the output node. Python tools use custom Python code:

The code in get_image is below:
from promptflow import tool
import json, base64, requests
def url_to_base64(image_url):
response = requests.get(image_url)
return 'data:image/jpg;base64,' + base64.b64encode(response.content).decode('utf-8')
@tool
def my_python_tool(image_json: str) -> str:
url = json.loads(image_json)["url"]
if url:
base64_string = url_to_base64(url)
else:
base64_string = url_to_base64("https://placehold.co/400/jpg?text=No+image")
return base64_string
The node executes the function that is marked with the @tool decorator and sends it the output from the LLM node. The code grabs the url and downloads and transforms the image to its base64 representation. You can see how the output from the LLM node is mapped to the image_json parameter below:
The code in get_url is similar. It just extracts the url as a string from the input JSON coming from the url.
The output node is the following:
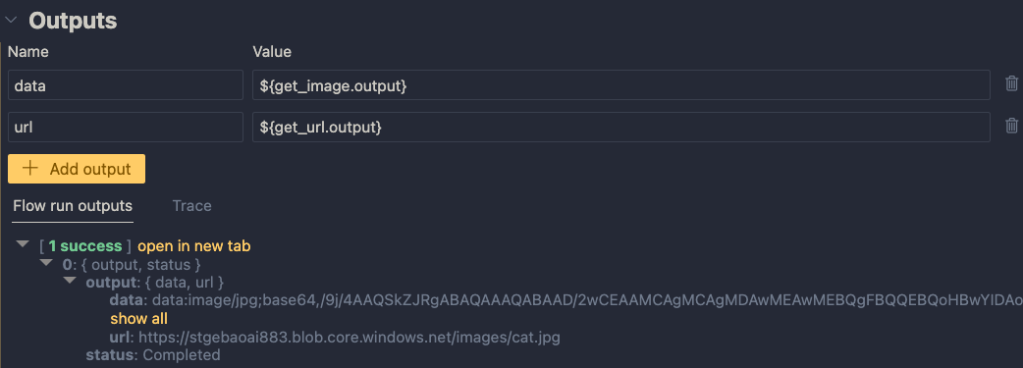
The output has two properties: data (the base64-encoded image) and the url to the image. Later, in the Python code that uses this flow, the output will be a Python dict with a data and url entry.
Using the flow in your application
Although you can host this flow as an API using either an Azure Machine Learning endpoint or a Docker container, we will simply embed the flow in our Python application and call it like a regular Python function.
Here is the code, which uses Streamlit for the UI:
from promptflow import load_flow
import streamlit as st
# load Prompt Flow from parent folder
flow_path = "../."
f = load_flow(flow_path)
# Streamlit UI
st.title('Search for an image')
# User input
user_query = st.text_input('Enter your query and press enter:')
if user_query:
# extract url from dict and wrap in img tag
flow_result = f(description=user_query)
image = flow_result["data"]
url = flow_result["url"]
img_tag = f'<a href="{url}"><img src="{image}" alt="image" width="300"></a>'
# just use markdown to display the image
st.markdown(f"🌆 Image URL: {url}")
st.markdown(img_tag, unsafe_allow_html=True)
To load the flow in your Python app as a function:
- import
load_flowfrom thepromptflowmodule - set a path to your flow (relative or absolute): here we load the flow that is in the parent directory that contains
flow.dag.yaml. - use
load_flowto create the function: above the function is calledf
When the user enters the query, you can simply use f(description="user's query...") to obtain the output. The output is a Python dict with a data and url entry.
In Streamlit, we can use markdown to display HTML directly using unsafe_allow_html=True. The HTML is simply an <img> tag with the src attribute set to the base64 representation of the image.
Connections
Note that the flow on my system uses two connections: one to connect to OpenAI and one to connect to Azure AI Search. By default, Prompt Flow stores these connections in a SQLite database in the .promptflow folder of your home folder. This means that the Streamlit app work on my machine but will not work anywhere else.
To solve this, you can override the connections in your app. See https://github.com/microsoft/promptflow/blob/main/examples/tutorials/get-started/flow-as-function.ipynb for more information about these overrides.
Conclusion
Embedding a flow as a function in a Python app is one of the easiest ways to use a flow in your applications. Although we used a straightforward Streamlit app here, you could build a FastAPI server that provides endpoints to multiple flows from one API. Such an API can easily be hosted as a container on Container Apps or Kubernetes as part of a larger application.
Give it a try and let me know what you think! 😉