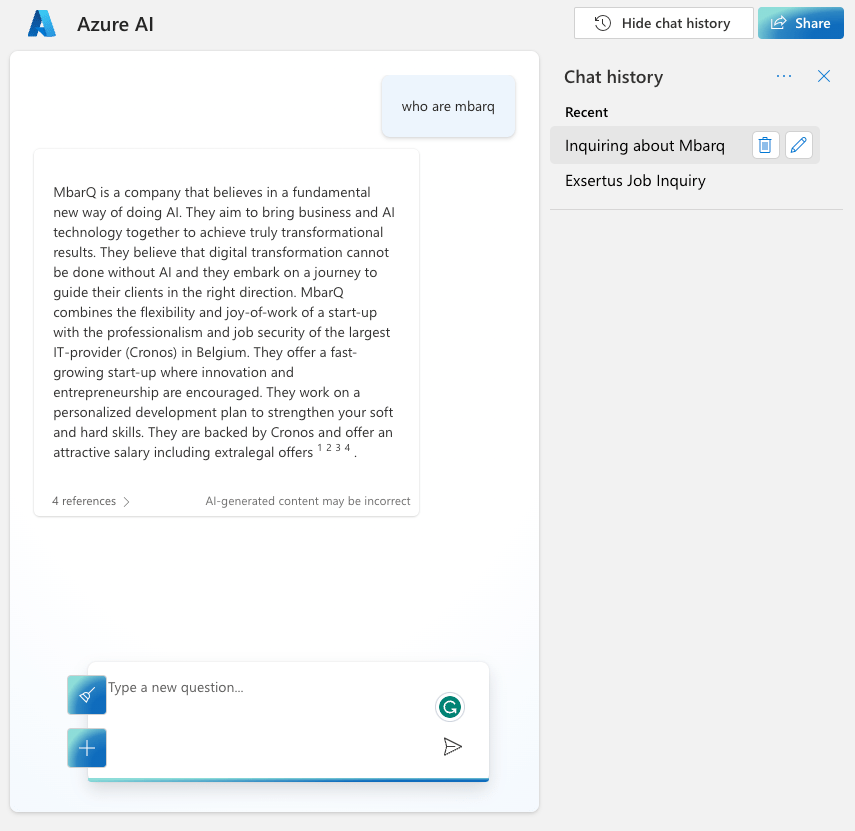
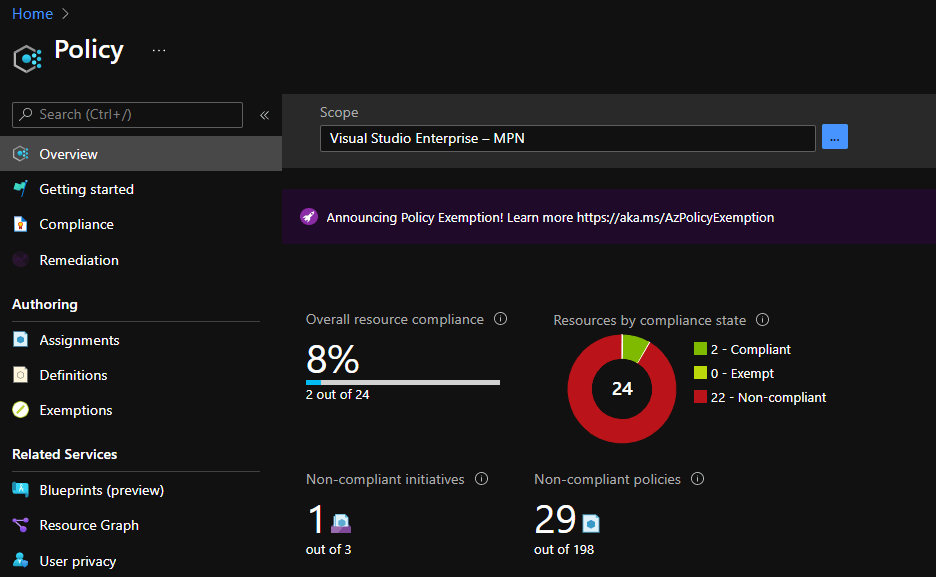
In the previous post, we looked at using Azure OpenAI Add your data from the Azure OpenAI Chat Playground. It is an easy-to-follow wizard to add documents to a storage account and start asking questions about them. From the playground, you can deploy a chat app to an Azure web app and you are good to go. The vector search is performed by an Azure Cognitive Search resource via an index that includes a vector next to other fields such as the actual content, the original URL, etc…
In this post, we will look at using this index from code and build a chat app using the Python Streamlit library.
All code can be found here: https://github.com/gbaeke/azure-cog-search
Requirements
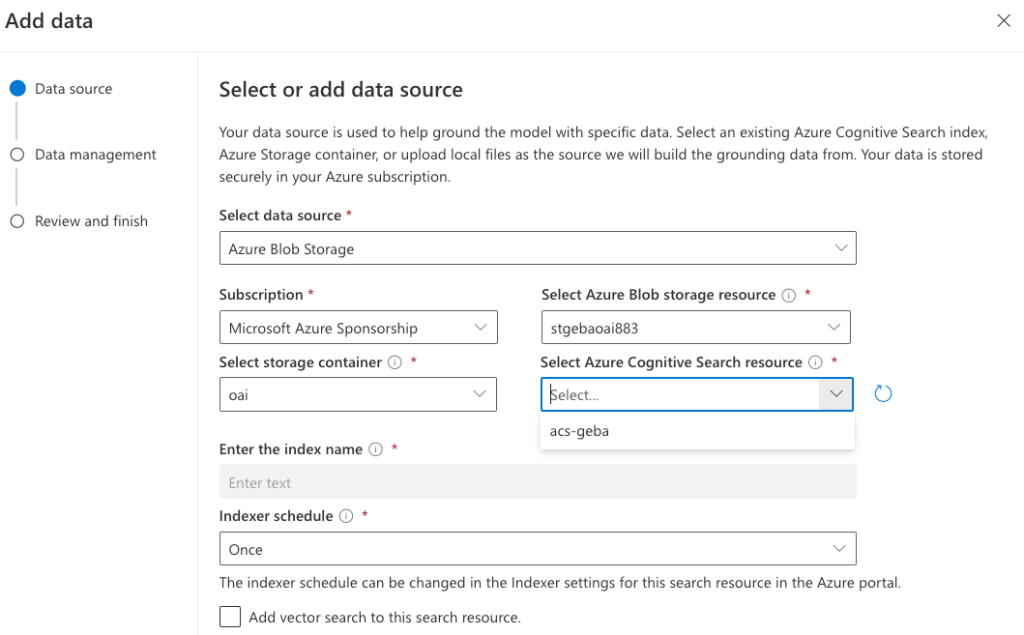
You need an Azure Cognitive Search resource with an index that supports vector search. Use this post to create one. Besides Azure Cognitive Search, you will need Azure OpenAI deployed with both gpt-4 (or 3.5) and the text-embedding-ada-002 embedding model. The embedding model is required to support vector search. In Europe, use France Central as the region.
Next, you need Python installed. I use Python 3.11.4 64-bit on an M1 Mac. You will need to install the following libraries with pip:
- streamlit
- requests
You do not need the OpenAI library because we will use the Azure OpenAI REST APIs to be able to use the extension that enables the Add your data feature.
Configuration
We need several configuration settings. The can be divided into two big blocks:
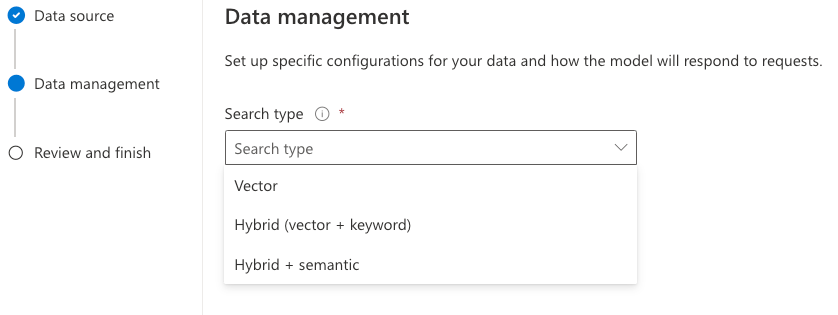
- Azure Cognitive Search settings: name of the resource, access key, index name, columns, type of search (vector), and more…
- Azure OpenAI settings: name of the model (e.g., gpt-4), OpenAI access key, embedding model, and more…
You should create a .env file with the following content:
AZURE_SEARCH_SERVICE = "AZURE_COG_SEARCH_SHORT_NAME"
AZURE_SEARCH_INDEX = "INDEX_NAME"
AZURE_SEARCH_KEY = "AZURE_COG_SEARCH_AUTH_KEY"
AZURE_SEARCH_USE_SEMANTIC_SEARCH = "false"
AZURE_SEARCH_TOP_K = "5"
AZURE_SEARCH_ENABLE_IN_DOMAIN = "true"
AZURE_SEARCH_CONTENT_COLUMNS = "content"
AZURE_SEARCH_FILENAME_COLUMN = "filepath"
AZURE_SEARCH_TITLE_COLUMN = "title"
AZURE_SEARCH_URL_COLUMN = "url"
AZURE_SEARCH_QUERY_TYPE = "vector"
# AOAI Integration Settings
AZURE_OPENAI_RESOURCE = "AZURE_OPENAI_SHORT_NAME"
AZURE_OPENAI_MODEL = "gpt-4"
AZURE_OPENAI_KEY = "AZURE_OPENAI_AUTH_KEY"
AZURE_OPENAI_TEMPERATURE = 0
AZURE_OPENAI_TOP_P = 1.0
AZURE_OPENAI_MAX_TOKENS = 1000
AZURE_OPENAI_STOP_SEQUENCE = ""
AZURE_OPENAI_SYSTEM_MESSAGE = "You are an AI assistant that helps people find information."
AZURE_OPENAI_PREVIEW_API_VERSION = "2023-06-01-preview"
AZURE_OPENAI_STREAM = "false"
AZURE_OPENAI_MODEL_NAME = "gpt-4"
AZURE_OPENAI_EMBEDDING_ENDPOINT = "https://AZURE_OPENAI_SHORT_NAME.openai.azure.com/openai/deployments/embedding/EMBEDDING_MODEL_NAME?api-version=2023-03-15-preview"
AZURE_OPENAI_EMBEDDING_KEY = "AZURE_OPENAI_AUTH_KEY"
Now we can create a config.py that reads these settings.
from dotenv import load_dotenv
import os
load_dotenv()
# ACS Integration Settings
AZURE_SEARCH_SERVICE = os.environ.get("AZURE_SEARCH_SERVICE")
AZURE_SEARCH_INDEX = os.environ.get("AZURE_SEARCH_INDEX")
AZURE_SEARCH_KEY = os.environ.get("AZURE_SEARCH_KEY")
AZURE_SEARCH_USE_SEMANTIC_SEARCH = os.environ.get("AZURE_SEARCH_USE_SEMANTIC_SEARCH", "false")
AZURE_SEARCH_TOP_K = os.environ.get("AZURE_SEARCH_TOP_K", 5)
AZURE_SEARCH_ENABLE_IN_DOMAIN = os.environ.get("AZURE_SEARCH_ENABLE_IN_DOMAIN", "true")
AZURE_SEARCH_CONTENT_COLUMNS = os.environ.get("AZURE_SEARCH_CONTENT_COLUMNS")
AZURE_SEARCH_FILENAME_COLUMN = os.environ.get("AZURE_SEARCH_FILENAME_COLUMN")
AZURE_SEARCH_TITLE_COLUMN = os.environ.get("AZURE_SEARCH_TITLE_COLUMN")
AZURE_SEARCH_URL_COLUMN = os.environ.get("AZURE_SEARCH_URL_COLUMN")
AZURE_SEARCH_VECTOR_COLUMNS = os.environ.get("AZURE_SEARCH_VECTOR_COLUMNS")
AZURE_SEARCH_QUERY_TYPE = os.environ.get("AZURE_SEARCH_QUERY_TYPE")
# AOAI Integration Settings
AZURE_OPENAI_RESOURCE = os.environ.get("AZURE_OPENAI_RESOURCE")
AZURE_OPENAI_MODEL = os.environ.get("AZURE_OPENAI_MODEL")
AZURE_OPENAI_KEY = os.environ.get("AZURE_OPENAI_KEY")
AZURE_OPENAI_TEMPERATURE = os.environ.get("AZURE_OPENAI_TEMPERATURE", 0)
AZURE_OPENAI_TOP_P = os.environ.get("AZURE_OPENAI_TOP_P", 1.0)
AZURE_OPENAI_MAX_TOKENS = os.environ.get("AZURE_OPENAI_MAX_TOKENS", 1000)
AZURE_OPENAI_STOP_SEQUENCE = os.environ.get("AZURE_OPENAI_STOP_SEQUENCE")
AZURE_OPENAI_SYSTEM_MESSAGE = os.environ.get("AZURE_OPENAI_SYSTEM_MESSAGE", "You are an AI assistant that helps people find information about jobs.")
AZURE_OPENAI_PREVIEW_API_VERSION = os.environ.get("AZURE_OPENAI_PREVIEW_API_VERSION", "2023-06-01-preview")
AZURE_OPENAI_STREAM = os.environ.get("AZURE_OPENAI_STREAM", "true")
AZURE_OPENAI_MODEL_NAME = os.environ.get("AZURE_OPENAI_MODEL_NAME", "gpt-35-turbo")
AZURE_OPENAI_EMBEDDING_ENDPOINT = os.environ.get("AZURE_OPENAI_EMBEDDING_ENDPOINT")
AZURE_OPENAI_EMBEDDING_KEY = os.environ.get("AZURE_OPENAI_EMBEDDING_KEY")
Writing the chat app
Now we will create chat.py. The diagram below summarizes the architecture:

Here is the first section of the code with explanations:
import requests
import streamlit as st
from config import *
import json
# Azure OpenAI REST endpoint
endpoint = f"https://{AZURE_OPENAI_RESOURCE}.openai.azure.com/openai/deployments/{AZURE_OPENAI_MODEL}/extensions/chat/completions?api-version={AZURE_OPENAI_PREVIEW_API_VERSION}"
# endpoint headers with Azure OpenAI key
headers = {
'Content-Type': 'application/json',
'api-key': AZURE_OPENAI_KEY
}
# Streamlit app title
st.title("🤖 Azure Add Your Data Bot")
# Keep messages array in session state
if "messages" not in st.session_state:
st.session_state.messages = []
# Display previous chat messages from history on app rerun
# Add your data messages include tool responses and assistant responses
# Exclude the tool responses from the chat display
for message in st.session_state.messages:
if message["role"] != "tool":
with st.chat_message(message["role"]):
st.markdown(message["content"])
A couple of things happen here:
- We import all the variables from config.py
- We construct the Azure OpenAI REST endpoint and store it in
endpoint; we use theextensions/chatendpoint here which supports the Add your data feature in API version2023-06-01-previewand higher - We configure the HTTP headers to send to the endpoint; the headers include the Azure OpenAI authentication key
- We print a title with Streamlit (
st.title) and define a messages array that we store in Streamlit’s session state - Because of the way Streamlit works, we have to print the previous messages of the chat each time the page reloads. We do that in the last part but we exclude the tool role. The
extensions/chatendpoint returns a tool response that contains the data returned by Azure Cognitive Search. We do not want to print the tool response. Together with the tool response, the endpoint returns an assistant response which is the response from the gpt model. We do want to print that response.
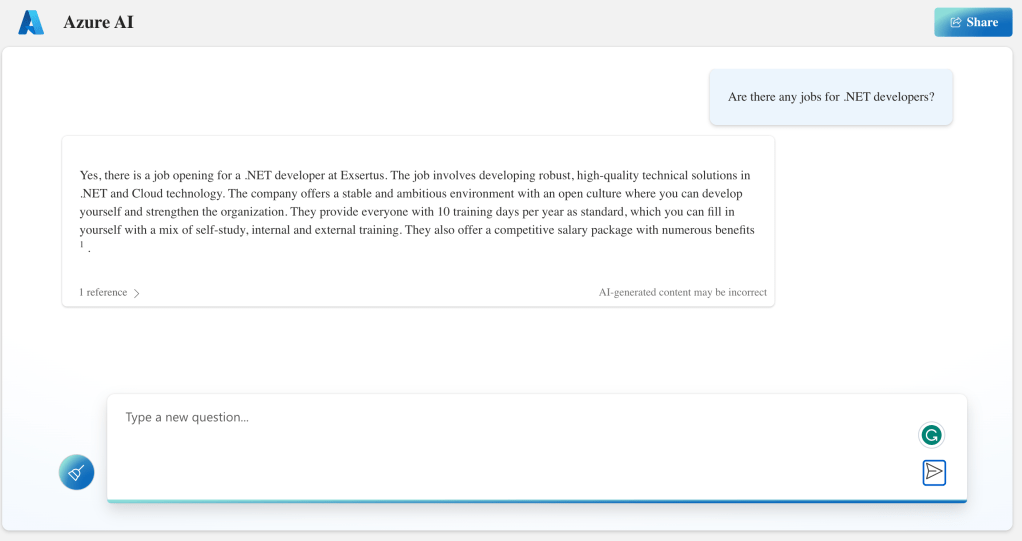
Now we can look at the code that gets executed each time the user asks a question. In the UI, the question box is at the bottom:

Whenever you type a question, the following code gets executed:
# if user provides chat input, get and display response
# add user question and response to previous chat messages
if user_prompt := st.chat_input():
st.chat_message("user").write(user_prompt)
with st.chat_message("assistant"):
with st.spinner("🧠 thinking..."):
# add the user query to the messages array
st.session_state.messages.append({"role": "user", "content": user_prompt})
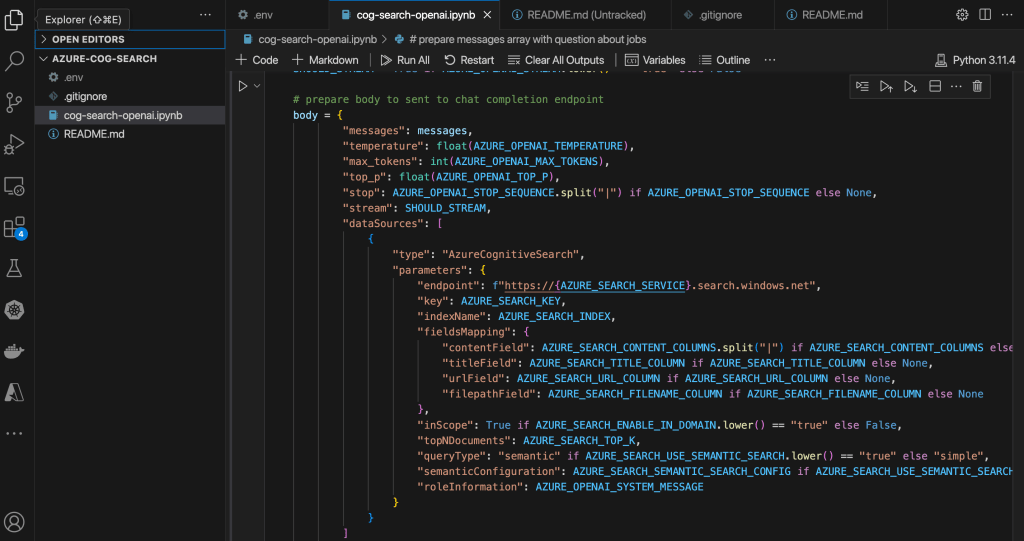
body = {
"messages": st.session_state.messages,
"temperature": float(AZURE_OPENAI_TEMPERATURE),
"max_tokens": int(AZURE_OPENAI_MAX_TOKENS),
"top_p": float(AZURE_OPENAI_TOP_P),
"stop": AZURE_OPENAI_STOP_SEQUENCE.split("|") if AZURE_OPENAI_STOP_SEQUENCE else None,
"stream": False,
"dataSources": [
{
"type": "AzureCognitiveSearch",
"parameters": {
"endpoint": f"https://{AZURE_SEARCH_SERVICE}.search.windows.net",
"key": AZURE_SEARCH_KEY,
"indexName": AZURE_SEARCH_INDEX,
"fieldsMapping": {
"contentField": AZURE_SEARCH_CONTENT_COLUMNS.split("|") if AZURE_SEARCH_CONTENT_COLUMNS else [],
"titleField": AZURE_SEARCH_TITLE_COLUMN if AZURE_SEARCH_TITLE_COLUMN else None,
"urlField": AZURE_SEARCH_URL_COLUMN if AZURE_SEARCH_URL_COLUMN else None,
"filepathField": AZURE_SEARCH_FILENAME_COLUMN if AZURE_SEARCH_FILENAME_COLUMN else None,
"vectorFields": AZURE_SEARCH_VECTOR_COLUMNS.split("|") if AZURE_SEARCH_VECTOR_COLUMNS else []
},
"inScope": True if AZURE_SEARCH_ENABLE_IN_DOMAIN.lower() == "true" else False,
"topNDocuments": AZURE_SEARCH_TOP_K,
"queryType": AZURE_SEARCH_QUERY_TYPE,
"roleInformation": AZURE_OPENAI_SYSTEM_MESSAGE,
"embeddingEndpoint": AZURE_OPENAI_EMBEDDING_ENDPOINT,
"embeddingKey": AZURE_OPENAI_EMBEDDING_KEY
}
}
]
}
# send request to chat completion endpoint
try:
response = requests.post(endpoint, headers=headers, json=body)
# there will be a tool response and assistant response
tool_response = response.json()["choices"][0]["messages"][0]["content"]
tool_response_json = json.loads(tool_response)
assistant_response = response.json()["choices"][0]["messages"][1]["content"]
# get urls for the JSON tool response
urls = [citation["url"] for citation in tool_response_json["citations"]]
except Exception as e:
st.error(e)
st.stop()
# replace [docN] with urls and use 0-based indexing
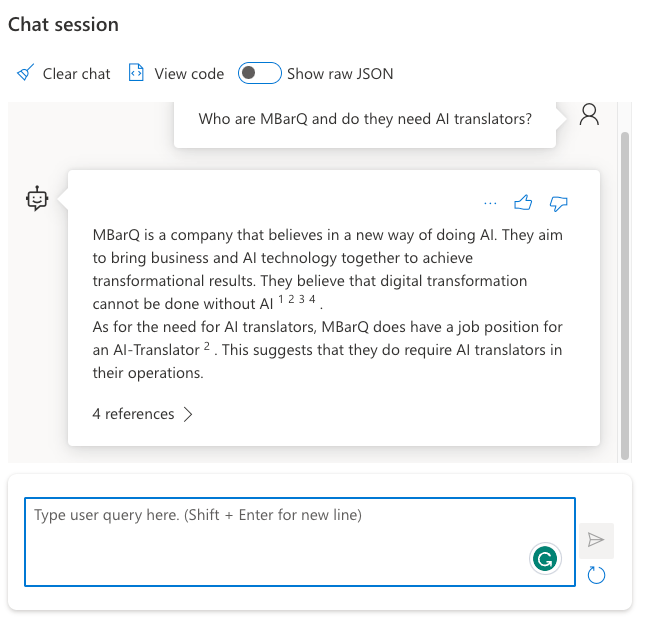
for i, url in enumerate(urls):
assistant_response = assistant_response.replace(f"[doc{i+1}]", f"[[{i}]({url})]")
# write the response to the chat
st.write(assistant_response)
# write the urls to the chat; gpt response might not refer to all
st.write(urls)
# add both responses to the messages array
st.session_state.messages.append({"role": "tool", "content": tool_response})
st.session_state.messages.append({"role": "assistant", "content": assistant_response})
When there is input, we write the input to the chat history on the screen and add it to the messages array. The OpenAI APIs expect a messages array that includes user and assistant roles. In other words, user questions and assistant (here gpt-4) responses.
With a valid messages array, we can send our payload to the Azure OpenAI extensions/chat endpoint. If you have ever worked with the OpenAI or Azure OpenAI APIs, many of the settings in the JSON body will be familiar. For example: temperature, max_tokens, and of course the messages themselves.
What’s new here is the dataSources field. It contains all the information required to perform a vector search in Azure Cognitive Services. The search finds content relevant to the user’s question (that was added last to the messages array). Because queryType is set to vector, we also need to provide the embedding endpoint and key. It’s required because the user question has to be vectorized in order to compare it with the stored vectors.
It’s important to note that the extensions/chat endpoint, together with the dataSources configuration takes care of a lot of the details:
- Perform a k-nearest neighbor search (k=5 here) to find 5 documents closely related to the user’s question
- It uses vector search for this query (could be combined with keyword and semantic search to perform a hybrid search but that is not used here)
- It stuffs the prompt to the GPT model with the relevant content
- It returns the GPT model response (assistant response) together with a tool response. The tool response contains citations that include URLs to the original content and the content itself.
In the UI, we print the URLs from these citations after modifying the assistant response to just return hyperlinked numbers like [0] and [1] for the citations instead of unlinked [doc1], [doc2], etc… In the UI, that looks like:

Note that this chat app is a prototype and does not include management of the messages array. Long interactions will reach the model’s token limit!
You can find this code on GitHub here: https://github.com/gbaeke/azure-cog-search.
Conclusion
Although still in preview, you now have an Azure-native solution that enables the RAG pattern with vector search. RAG stands for Retrieval Augmented Generation. Azure Cognitive Search is a fully managed service that stores the vectors and performs similarity searches. There is no need to deploy a 3rd party vector database.
There is no need for specific libraries to implement this feature because it is all part of the Azure OpenAI API. Microsoft simply extended that API to add data sources and takes care of all the behind-the-scenes work that finds relevant content and adds it to your prompt.
If, for some reason, you do not want to use the Azure OpenAI API directly and use something like LangChain or Semantic Kernel, you can of course still do that. Both solutions support Azure Cognitive Search as a vector store.